SPERONI - CLAWS
Un’articolo molto interessante sugli speroni dei cani
Da leggere assolutamente, soprattutto chi fa sport col proprio cane
Sono un veterinario che lavora esclusivamente coi cani sportivi, sviluppando piani di riabilitazione per cani infortunati o cani che hanno subito un’operazione a causa di un’infortunio sportivo.
Ho visto così tanti cani, specialmente cani da trial/caccia e agility, che hanno avuto artrite carpale cronica, spesso così seria da doversi ritirare o almeno essere gestiti con cura per il resto della loro carriera.
Degli oltre 30 cani che ho visto con questa artrite carpale, solo uno aveva gli speroni, agli altri erano stati rimossi.
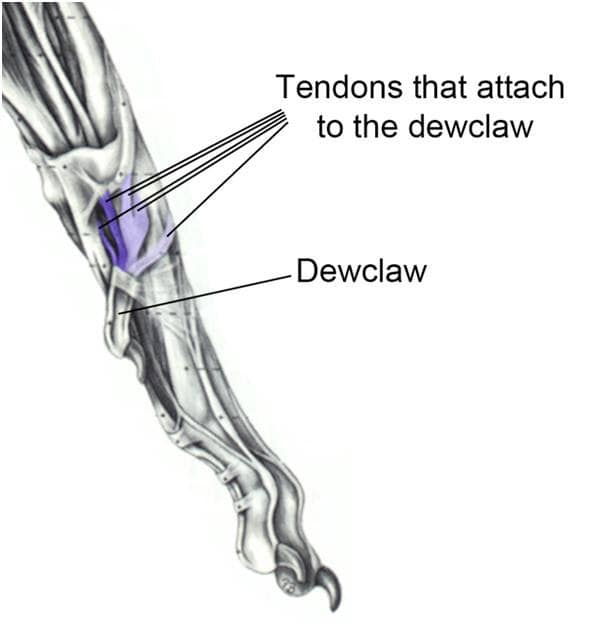
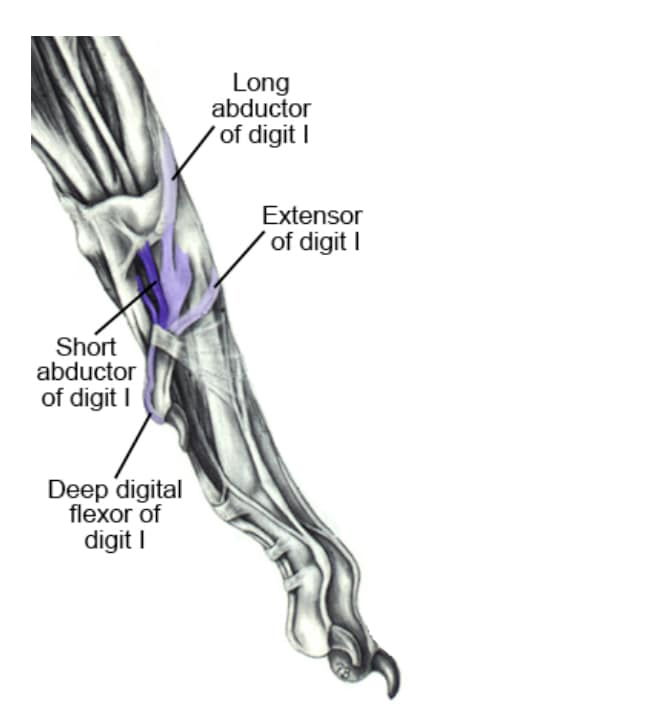
Se guardate un libro di anatomia (Miller’s Guide to the Anatomy of dogs è uno eccellente, vedi figura in basso) vedrete che ci sono 5 tendini attaccati allo sperone.
Ovviamente all’altro capo di un tendine c’è un muscolo, quindi questo significa che se tagliate lo sperone, ci sono 5 fasci muscolari che si atrofizzeranno per il disuso.
Questi muscoli indicano che gli speroni hanno una funzione. Questa funzione è di prevenire la torsione della zampa.
Ogni volta che il piede appoggia per terra, specialmente quando il cane corre (galoppa), lo sperone è in appoggio col terreno. Se il cane deve girare, lo sperone affonda nel terreno per supportare la parte inferiore della zampa e prevenire la torsione. Se il cane non ha lo sperone la zampa ruota in torsione.
Una vita di questo movimento e il risultato può essere artrite al carpo.
Ricordate: il cane svolge l'attività noncurante e le pressioni sulla gamba devono andare da qualche parte.
Possono essere assorbite dallo sperone o si muoveranno su e giù per la zampa fino alle dita dei piedi, carpi, gomiti e spalle.
Forse stai pensando: "Non ho mai avuto uno dei miei cani con dolore o artrite carpale". Bene, dobbiamo ricordare che i cani, per loro stessa natura, non ci parlano di dolore da lieve a moderato. Se un infermiere del pronto soccorso chiedesse a un cane di dire il livello del suo dolore su una scala da 0 a 10, con 10 che è il peggiore, la sua scala sarebbe 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6, 7 ,8, 9, 10. La maggior parte dei nostri cani, specialmente se hanno a che fare con un dolore a insorgenza graduale, ci convivono e non si lamentano a meno che non sia lancinante. Ma quando palpo le articolazioni carpali dei cani più anziani senza speroni, quasi sempre suscito dolore con una manipolazione relativamente minima.
Per quanto riguarda la possibilità di lesioni agli speroni, la maggior parte dei veterinari dirà che tali lesioni in realtà non sono affatto molto comuni. E se si verificano, vengono trattati come qualsiasi altra lesione. Secondo me è molto meglio affrontare un infortunio piuttosto che tagliare gli speroni di tutti i cani "nel caso in cui”.
L’immagine mostra il lato mediale della zampa anteriore sinistra di un cane e fa vedere bene i cinque tendini che si attaccano al sperone.”
ARTICOLO ORIGINALE
Do the Dew(claws)?
M. Christine Zink DVM, PhD, DACVSMR
I am a vet that works exclusively with performance dogs, developing rehabilitation programs for injured dogs or dogs that have had surgery as a result of performance-related
injuries. I have seen many dogs now, especially field trial/hunt test and agility dogs, that have had chronic carpal arthritis, frequently so severe that they have to be retired or at least carefully managed for the rest of their careers. Of the over 30 dogs I have seen with carpal arthritis, only one has had dewclaws. The others have all had them removed.
If you look at an anatomy book (Miller’s Guide to the Anatomy of Dogs is an excellent one – see figure below) you will see that there are 5 tendons attached to the dewclaw. Of course, at the other end of a tendon is a muscle, and that means that if you cut off the dew claws, there are 5 muscle bundles that will become atrophied from disuse.
Those muscles indicate that the dewclaws have a function. That function is to prevent torque on the leg. Each time the foot lands on the ground, particularly when the dog is cantering or galloping, the dewclaw is in touch with the ground. If the dog then needs to turn, the dewclaw digs into the ground to support the lower leg and prevent torque. If the dog doesn’t have a dewclaw, the leg twists. A lifetime of that and the result can be carpal arthritis. Remember: the dog is doing the activity regardless, and the pressures on the leg have to go somewhere.
They can be absorbed by the dewclaw, or they will move up and down the leg to the toes, carpus, elbow, and shoulders.
Perhaps you are thinking, “I never have had one of my dogs have carpal pain or arthritis.” Well, we need to remember that dogs, by their very nature, do not tell us about mild to moderate pain. If a dog was to be asked by an emergency room nurse to give the level of his pain on a scale from 0 to 10, with 10 being the worst, their scale would be 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10. Most of our dogs, especially if they deal with pain that is of gradual onset, just deal with it and don’t complain unless it is excruciating. But when I palpate the carpal joints of older dogs without dewclaws, I almost always elicit pain with relatively minimal manipulation.
As to the possibility of injuries to dew claws. Most veterinarians will say that such injuries actually are not very common at all. And if they do occur, then they are dealt with like any other injury. In my opinion, it is far better to deal with an injury than to cut the dew claws off of all dogs “just in case.”
Anatomical diagram viewing the medial side of a dog’s left front leg demonstrating the five tendons that attach to the dewclaw.



